15 posts
On the basis of class, there can be three types of inheritance in java: single, multilevel and hierarchical.
In java programming, multiple and hybrid inheritance is supported through interface only.
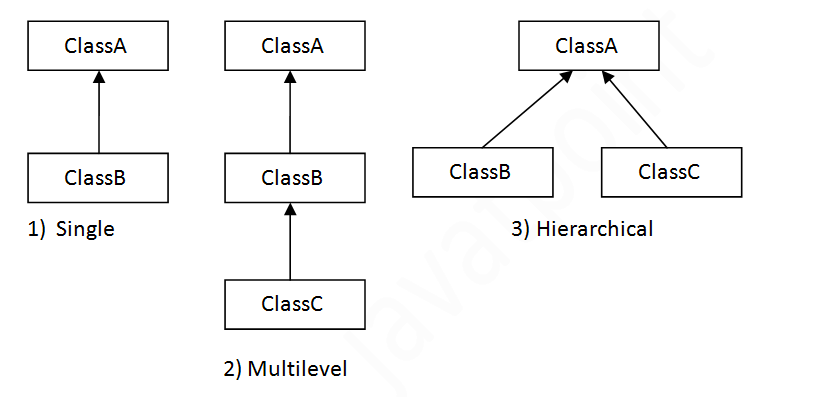
In single inheritance, subclasses inherit the features of one superclass. In image below, the class A serves as a base class for the derived class B.
//SingleInheritance.java
class Animal
{
void eat()
{
System.out.println("eating...");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal
{
void bark()
{
System.out.println("barking...");
}
}
class SingleInheritance
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Dog d=new Dog();
d.bark();
d.eat();
}
}
//MultilevelInheritance.java
class Animal
{
void eat()
{
System.out.println("eating...");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal
{
void bark()
{
System.out.println("barking...");
}
}
class BabyDog extends Dog
{
void weep()
{
System.out.println("weeping...");
}
}
class MultilevelInheritance
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
BabyDog d=new BabyDog();
d.weep();
d.bark();
d.eat();
}
}
In Hierarchical Inheritance, one class serves as a superclass (base class) for more than one sub class.
//HierarchicalInheritance.java
class Animal
{
void eat()
{
System.out.println("eating...");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal
{
void bark()
{
System.out.println("barking...");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal
{
void meow()
{
System.out.println("meowing...");
}
}
class HierarchicalInheritance
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Cat c=new Cat();
c.meow();
c.eat();
}
}
To reduce the complexity and simplify the language, multiple inheritance is not supported in java.
Consider a scenario where A, B, and C are three classes. The C class inherits A and B classes. If A and B classes have the same method and you call it from child class object, there will be ambiguity to call the method of A or B class.
Since compile-time errors are better than runtime errors, Java renders compile-time error if you inherit 2 classes. So whether you have same method or different, there will be compile time error.
class A
{
void msg()
{
System.out.println("Hello");
}
}
class B
{
void msg()
{
System.out.println("Welcome");
}
}
class C extends A,B //suppose if it were
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
C obj=new C();
obj.msg();//Now which msg() method would be invoked?
}
}
Please log in to leave a comment.