15 posts
An interface in java is a blueprint of a class. It has static constants and abstract methods.The interface in Java is a mechanism to achieve abstraction and multiple inheritance in Java.
Like a class, an interface can have methods and variables, but the methods declared in interface are by default abstract (only method signature, no body).
To declare an interface, use interface keyword. It is used to provide total abstraction.
Java Interface also represents the IS-A relationship.
It cannot be instantiated just like the abstract class.
Since Java 8, we can have default and static methods in an interface.
Since Java 9, we can have private methods in an interface.
interface <interface_name>
{
// declare constant fields
// declare methods that abstract
}
There are mainly three reasons to use interface.

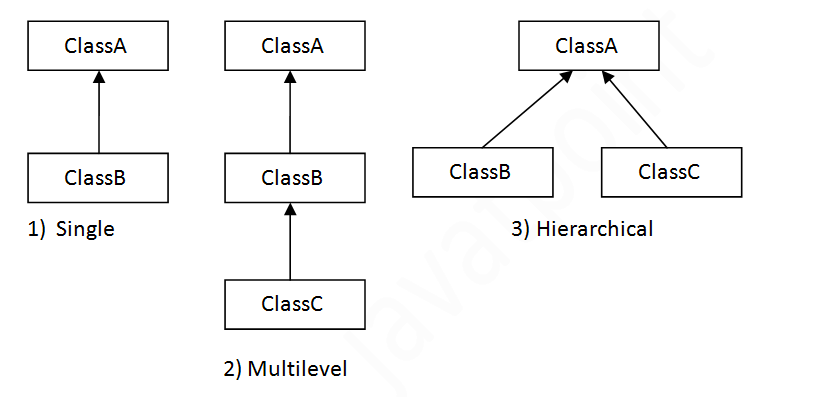
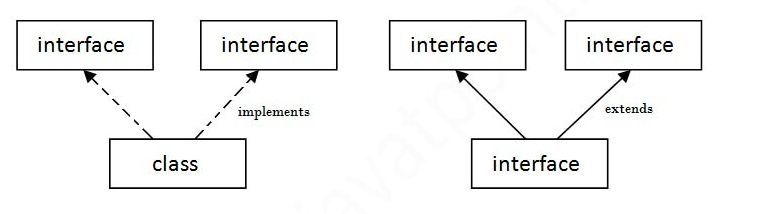
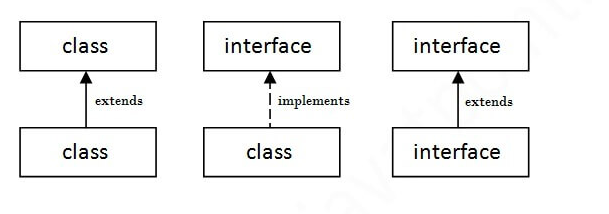
A class extends another class, an interface extends another interface, but a class implements an interface.
Here the Printable interface has only one method, and its implementation is provided in the Draw class.
//printable.java
interface printable
{
void print();
}
//Draw.java
class Draw implements printable
{
public void print()
{
System.out.println("Hello");
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
A6 obj = new A6();
obj.print();
}
}
Please log in to leave a comment.