15 posts
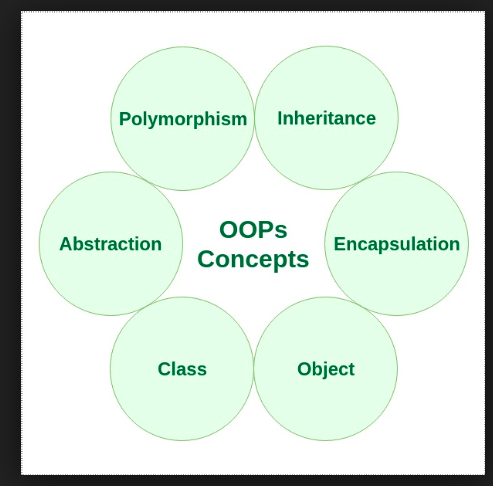
Object-Oriented Programming or OOPs refers to languages that uses objects in programming. It mainly focus on implementing real-world entities like Inheritance,hiding,Polymorphism etc in Programming.The main aim of OOPs is to bind together the data and the functions that operate on them so that no other part of the code can access this data except that function.
An object in Java is the physical as well as a logical entity, whereas, a class in Java is a logical entity only.

An entity that has state and behavior is known as an object e.g., chair, bike, marker, pen, table, car, etc. It can be physical or logical (tangible and intangible). The example of an intangible object is the banking system.
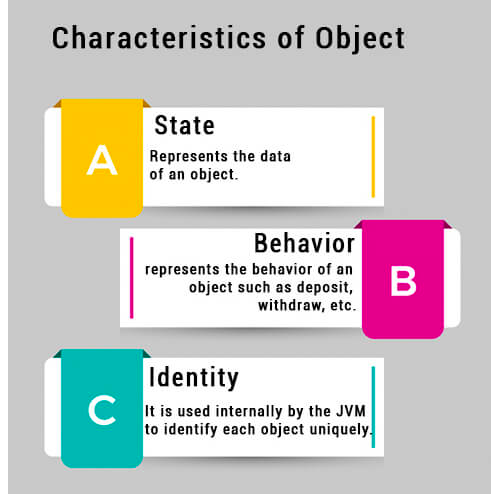
For Example, Pen is an object. Its name is Reynolds; color is white, known as its state. It is used to write, so writing is its behavior.
"An object is an instance of a class".A class is a template or blueprint from which objects are created. So, an object is the instance(result) of a class.
A class is a group of objects which have common properties. It is a template or blueprint from which objects are created. It is a logical entity. It can't be physical.
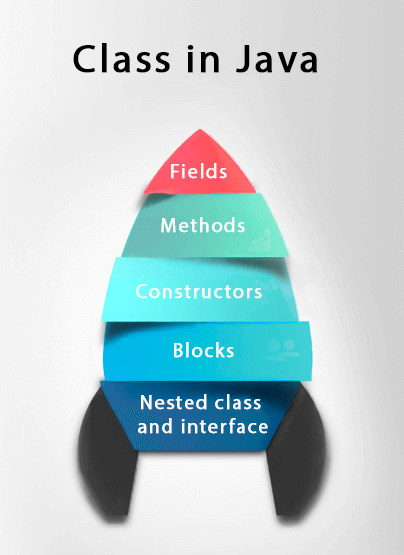
A class in Java can contain:
Here, we have created a Student class which has two data members id and name. We are creating the object of the Student class by new keyword and printing the object's value.
//Student.java
class Student
{
int id;
String name;
public static void main(String args[])
{
Student s1=new Student();//creating an object of Student
System.out.println(s1.id);//accessing member through reference variable
System.out.println(s1.name);
}
}
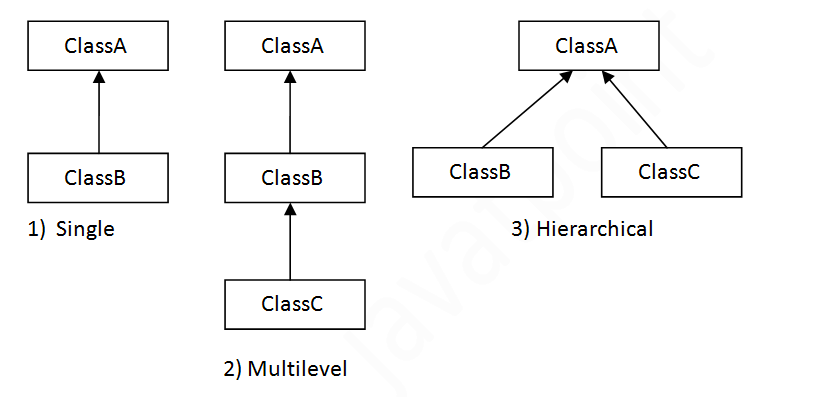
Inheritance represents the "IS-A" relationship which is also known as a parent-child relationship.
class Subclass-name extends Superclass-name
{
//methods
}
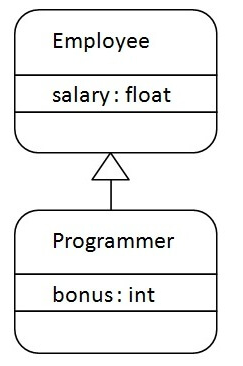
//Employee.java
class Employee{
float salary=40000;
}
//Programmer.java
class Programmer extends Employee
{
int bonus=10000;
public static void main(String args[])
{
Programmer p=new Programmer();
System.out.println("Programmer salary is:"+p.salary);
System.out.println("Bonus of Programmer is:"+p.bonus);
}
}
Polymorphism is a concept by which we can perform a "single action in different ways". Polymorphism is derived from 2 Greek words: poly and morphs. The word "poly" means many and "morphs" means forms. So polymorphism means many forms.
There are two types of polymorphism in Java: compile-time polymorphism and runtime polymorphism. We can perform polymorphism in java by method overloading and method overriding.
Polymorphism that is resolved during compiler time is known as static or compile-time polymorphism. Method overloading is an example of compile time polymorphism.
Method Overloading: This allows us to have more than one method having the same name, if the parameters of methods are different in number, sequence and data types of parameters.
public class Sum
{
public int sum(int x, int y)
{
return (x + y);
}
public int sum(int x, int y, int z)
{
return (x + y + z);
}
public double sum(double x, double y)
{
return (x + y);
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Sum s = new Sum();
System.out.println(s.sum(10, 20));
System.out.println(s.sum(10, 20, 30));
System.out.println(s.sum(10.5, 20.5));
}
}
First we will understand what is meant by Up Casting,
If the reference variable of Parent class refers to the object of Child class, then it is known as upcasting.
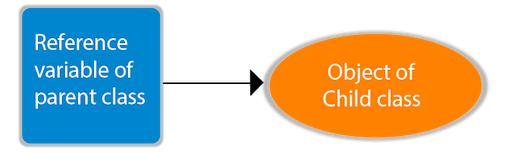
For Example:
class A{}
class B extends A{}
A a=new B();//this is upcasting
Runtime Polymorphism or Dynamic Method Dispatch is a process in which a call to an overridden method is resolved at runtime rather than compile-time.
In this process, an overridden method is called through the reference variable of a superclass. The determination of the method to be called is based on the object being referred to by the reference variable.
//ABC.java
class ABC
{
public void myMethod()
{
System.out.println("Overridden Method");
}
}
//XYZ.java
public class XYZ extends ABC
{
public void myMethod()
{
System.out.println("Overriding Method");
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
ABC obj = new XYZ();
obj.myMethod();
}
}
Encapsulation in Java is a mechanism of wrapping the data (variables) and code acting on the data (methods) together as a single unit. In encapsulation, the variables of a class will be hidden from other classes, and can be accessed only through the methods of their current class. Therefore, it is also known as "data hiding".
we can achieve Encapsulation in two different ways in Java:
1.Declare the variables of a class as private.
2.Provide public setter and getter methods to modify and view the variables values.
//Encapsulation.java
public class Encapsulation
{
private String name;
private String idNum;
private int age;
public int getAge()
{
return age;
}
public String getName()
{
return name;
}
public String getIdNum()
{
return idNum;
}
public void setAge( int newAge)
{
age = newAge;
}
public void setName(String newName)
{
name = newName;
}
public void setIdNum( String newId)
{
idNum = newId;
}
}
The public setXXX() and getXXX() methods are the access points of the instance variables of the Encapsulation class. Normally, these methods are referred as getters and setters. Therefore, any class that wants to access the variables should access them through these getters and setters.
The variables of the Encapsulation Class can be accessed using:
//RunEncapsulation.java
public class RunEncapsulation
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Encapsulation encap = new Encapsulation();
encap.setName("James");
encap.setAge(20);
encap.setIdNum("12343ms");
System.out.print("Name : " + encap.getName() + " Age : " + encap.getAge());
}
}
"Abstraction" is a process of hiding the implementation details and showing only functionality to the user.
Another way, it shows only essential things to the user and hides the internal details, for example, sending SMS where you type the text and send the message. You don't know the internal processing about the message delivery.
Abstraction lets you focus on what the object does instead of how it does it.
There are two ways to achieve abstraction in java
A class which is declared as abstract is known as an "abstract class". It can have abstract and non-abstract methods. It needs to be extended and its method implemented. It cannot be instantiated.
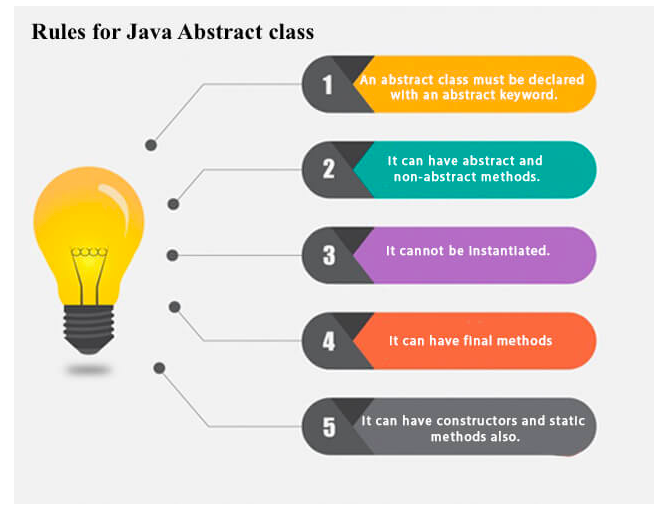
//Bike.java
abstract class Bike
{
abstract void run();
}
//Honda.java
class Honda extends Bike
{
void run()
{
System.out.println("running safely");
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Bike obj = new Honda4();
obj.run();
}
}
Please log in to leave a comment.